The Mediterranean Diet is a valuable cultural heritage that is much more than just a tasty and healthy dietary pattern. It is a balanced lifestyle that includes recipes, cooking methods, celebrations, customs, local products and various activities.
Among the many health benefits this dietary pattern has to offer, we can highlight its characteristic type of fat(olive oil, fish and nuts), the proportion of macronutrients that can be found in its recipes (such as grains and vegetable base with meat or similar as a “garnish”) and rich in micronutrients thanks to the use of seasonal vegetables, herbs and spices.
This is what the UNESCO recognised and celebrated by including the Mediterranean Diet as one of the items on the Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. The healthy eating pattern that is the Mediterranean Diet is perfectly compatible with the pleasure of tasting delicious dishes.
The Pyramid
THE NEW IMAGE INCORPORATES QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ELEMENTS REGARDING FOOD SELECTION.
THE TRADITIONAL MEDITERRANEAN DIET PYRAMID HAS BEEN UPDATED TO SUIT CURRENT LIFESTYLES.
BY INITIVATIVE OF THE MEDITERRANEAN DIET FOUNDATION AN DIN COLLABORATION WITH MANY INTERNATIONAL ORGANISATIONS, a group of experts from various disciplines, from nutrition to anthropology, sociology to agriculture, have agreed on this new representation enriched to include qualitative elements.
The new pyramid follows the previous pattern: at the base, foods that should sustain the diet, and at the upper levels, foods to be eaten in moderate amounts. Moreover, social and cultural elements characteristic of the Mediterranean way of life are incorporated in the graphic design. It is not just about prioritizing some food groups from others, but also paying attention to the way of selecting, cooking and eating. It also reflects the composition and number of servings of main meals.
One or two servings per meal in the form of bread, pasta, rice, couscous and others. Preferably whole grain, since some valuable nutrients (magnesium, phosphorus, etc.) and fibre can be lost during processing. Vegetables should be presents at lunch and dinner; more or equal two servings per meal, at least one of the serving should be raw.
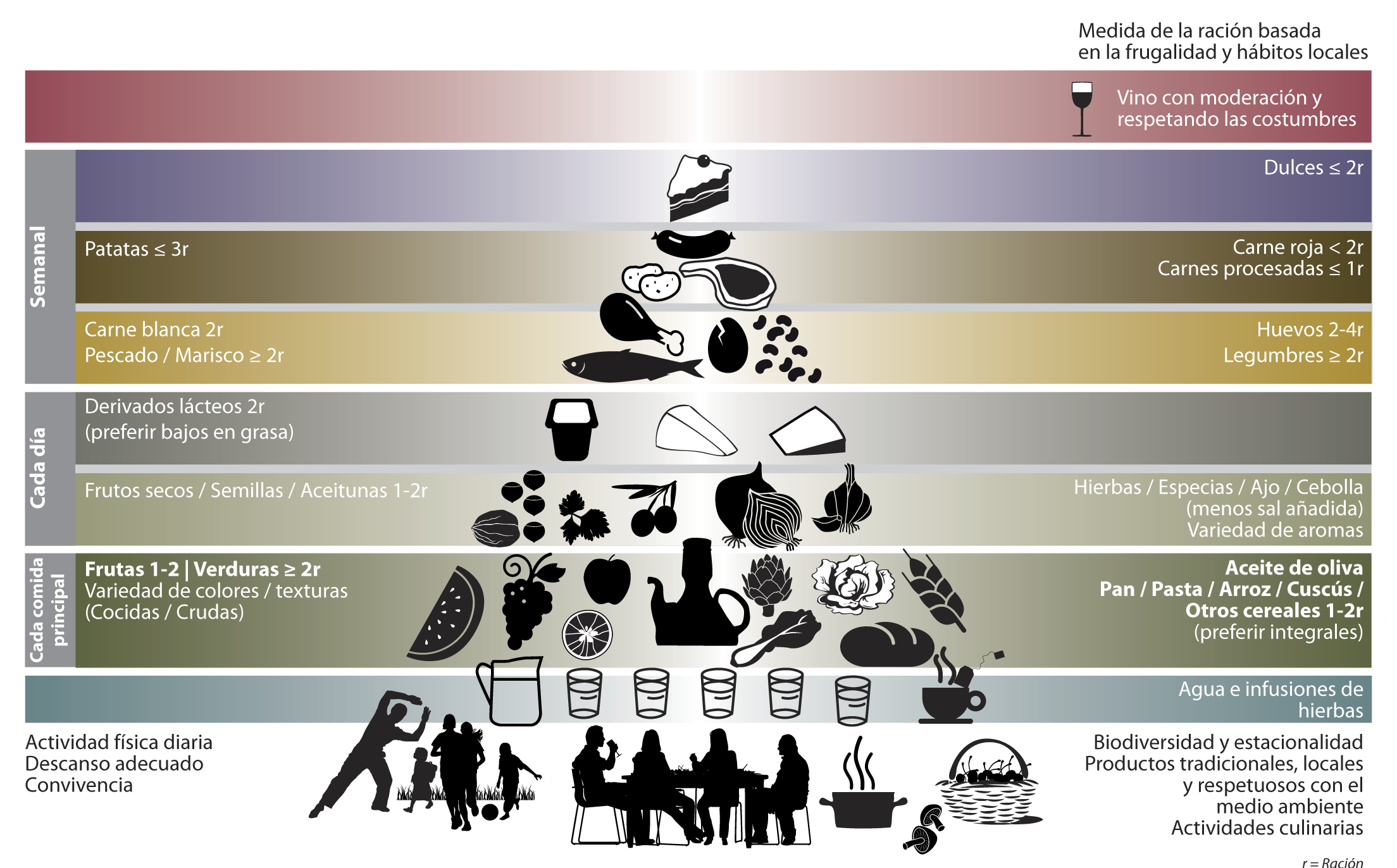
A daily intake of 1.5 to 2 litres of water should be guarantied. A good hydration is essential to maintain the corporal water equilibrium, although needs may vary among people because of age, physical activity, personal circumstances and weather conditions.
10 BASICS
1- Use olive oil as your main source of added fat.
Mediterranean cuisine. It is rich in Vitamin E, beta-carotenes and a type of vegetal fat (monounsaturated) that helps prevent cardiovascular diseases. It represents a treasure in the Mediterranean Diet and has remained through centuries among regional gastronomical traditions, conferring dishes unique tastes and aromas.
2- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables; fruits, vegetables, legumes and nuts.
Fruits and vegetables are a main source of vitamins, minerals and fibre in our diets and they also provide us with a large amount of water. It is very important to consume 5 servings of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis. Thanks to elevated content of antioxidants and fibre, they can contribute to prevent various cardiovascular diseases and certain cancers, among others.
3- Bread and other grain products (pasta, rice, and whole grains) should be a part of your everyday diet.
Daily consumption of pasta, rice and grain products in general is essential due to their high content in carbohydrates. They provide us with an important amount of energy needed for our daily activities. We should keep in mind that whole grain products provide us more fibre, vitamins and minerals.
4- Foods that have undergone minimal processing, that are fresh and locally produced are best.
It is important to take advantage of in-season products since they are at their best moment; in terms of both nutrients and aroma and flavour.
5- Consume dairy products on a daily basis, mainly yogurt and cheese.
Dairy products are excellent sources of proteins, minerals (calcium, phosphorus, etc.) and vitamins. Fermented dairy products (yogurt, bio, etc.) are associated to a series of health benefits since they contain live microorganismes capable of improving the balance of our intestinal microflora.
6- Red meat should be consumed in moderation and if possible as a part of stews and other recipes.
Processed meat should be consumed in small amounts and as a part of sandwiches and other dishes. Meat contains proteins, iron and animal fat in variable quantities. An excessive intake of animal fat is not healthy. Therefore, small amounts of meat are recommended, lean meat whenever possible and as a part of a dish with a cereal and vegetable base.
7- Consume fish abundantly and eggs in moderation.
It is recommended to consume fatty (dark meat) fish at least once or twice a week since it’s fat –even though of animal origin- has properties quite similar to those of vegetable origin which are known to protect against heart disease. Eggs are rich in high quality proteins, fat and many vitamins and minerals that make them a very complete food item. Eating eggs three or four times a week is a good alternative to fish and meat.
8- Fresh fruit should be your everyday dessert and, sweets, cakes and dairy desserts should be consumed only on occasion.
Fresh fruit should be your usual dessert, before sweets and pastries. Fruits are very nutritious and bring colour and flavour to our diet as well as being a health snack alternative.
9- Water is the beverage par excellence in the Mediterranean Diet.
Wine should be taken in moderations and with meals. Water is fundamental in our diet. Wine is a traditional part of the Mediterranean Diet that can provide health benefits but it must be taken with moderation and as a part of a balanced diet.
10- Be physically active every day, since it is just as important as eating well.
Keeping physically fit and doing physical activity adapted to our needs every day is key in keeping healthy.



